Introduction and Overview¶
Note
consider the usage of logging when executing long running commands:
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,
format='%(asctime)s %(message)s')
Run FEMAG with FSL¶
Run a single calculation (single process):
workdir = os.path.join(os.path.expanduser('~'), 'femag')
femag = femagtools.Femag(workdir)
femag.run('femag.fsl')
Run several calculations in parallel (multi processes):
engine = femagtools.multiproc.Engine()
job = engine.create_job(workdir)
for fsl in ('femag-1.fsl', 'femag-2.fsl', 'femag-3.fsl'):
task = job.add_task()
task.add_file(fsl)
numtasks = engine.submit()
status = engine.join()
Read BCH/BATCH File¶
Read a BCH file and print the machine torque:
bch = femagtools.read_bchfile('TEST_002.BCH')
print(bch.machine['torque'])
Convert a BCH file to XML by command line:
python -m femagtools.bchxml TEST_002.BCH
This command creates the file TEST_002.xml
Read I7/ISA7 File¶
Read an ISA7/I7 File (filename extension is optional):
>>> isa = isa7.read('foo')
Print Node coordinates:
>>> n = isa.nodes[0]
>>> print(n.x)
(0.03380740433931351)
>>> print(n.y)
(0.009058667346835136)
>>> print(n.xy)
(0.03380740433931351, 0.009058667346835136)
Get an Element by key:
>>> el = isa.elements[0]
Inspect Element properties:
>>> el.mag
(0.8485281467437744, 0.8485281467437744)
>>> el.reluc
(0.9523810148239136, 0.9523810148239136)
Get Node coordinates of Element:
>>> el_coords = [v.xy for v in el.vertices]
>>> print(el_coords)
[(0.036389999091625214, 1.142020034095026e-09),
(0.03499503806233406, 0.0005893968627788126),
(0.03500000014901161, 0.0)]
Get a SuperElement by Element:
>>> spel = isa.superelements[el.se_key]
>>> el in spel.elements
True
Plot SuperElements:
from femagtools import isa7
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from femagtools import plot
isa = isa7.read("PM_130_L4.ISA7")
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, aspect='equal')
plot.spel(isa)
plt.show()
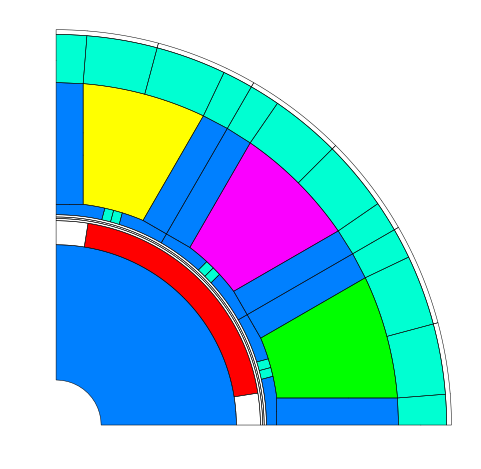
Create FSL and/or invoke FEMAG with Model Parameters¶
Create a FE model from the templates stator1 and magnetSector:
machine = dict(
name = "PM 130 L4",
lfe = 0.1,
poles = 4,
outer_diam = 0.13,
bore_diam = 0.07,
inner_diam = 0.015,
airgap = 0.001,
stator = dict(
num_slots = 12,
mcvkey_yoke = "dummy",
rlength = 1.0,
stator1 = dict(
slot_rf1 = 0.057,
tip_rh1 = 0.037,
tip_rh2 = 0.037,
tooth_width = 0.009,
slot_width = 0.003)
),
magnet = dict(
mcvkey_shaft = "dummy",
mcvkey_yoke = "dummy",
magnetSector = dict (
magn_num = 1,
magn_width_pct = 0.8,
magn_height = 0.004,
magn_shape = 0.0,
bridge_height = 0.0,
magn_type = 1,
condshaft_r = 0.02,
magn_ori = 2,
magn_rfe = 0.0,
bridge_width = 0.0,
magn_len = 1.0 )
),
windings = dict(
num_phases = 3,
num_wires = 100,
coil_span = 3.0,
num_layers = 1)
)
fsl = femagtools.create_fsl(model)
with open('femag.fsl', 'w') as f:
f.write('\n'.join(fsl))
After opening this file in FEMAG the shown geometry is created:
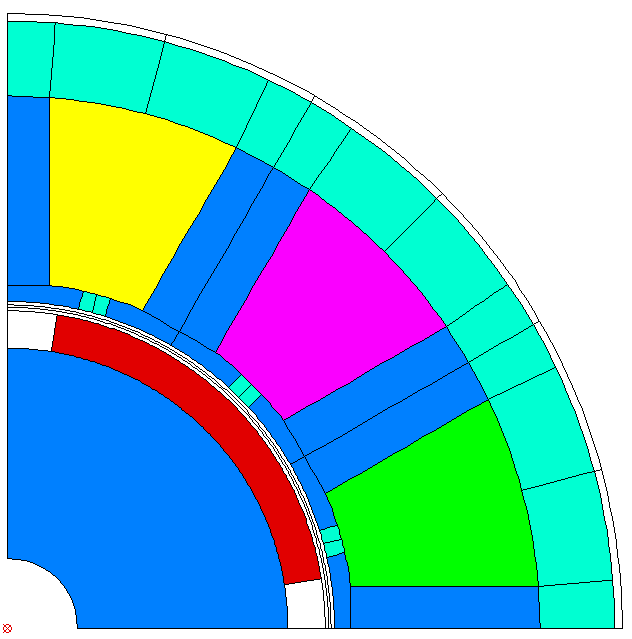
The same machine and operating parameters can be used to run FEMAG directly:
femag = femagtools.Femag(workdir)
operatingConditions = dict(
calculationMode="pm_sym_fast",
current=50.0,
angl_i_up=0.0,
speed=50.0,
wind_temp=60.0,
magn_temp=60.0)
r = femag(machine,
operatingConditions)
print('Torque [Nm] = {}'.format(r.machine['torque']))
Evaluate PM/Reluctance machine characteristics¶
Definition of the PM or Reluctance machine with Ld,Lq parameters:
p = 4
r1 = 0.0806
ls = 0.0
ld = [1.4522728e-3, 1.4522728e-3]
lq = [3.2154e-3, 3.8278836e-3]
psim = [0.11171972, 0.11171972]
i1 = [80.0]
beta = [0.0, -41.1]
pm = femagtools.machine.PmRelMachineLdq(3, p,
psim,
ld,
lq,
r1,
beta,
i1)
Calculation of minimal current and frequency at given torque and max voltage:
tq = 170.0
u1 = 340.0
iqx, idx = pm.iqd_torque(tq)
w1 = pm.w1_u(u1, idx, iqx)
i1 = np.linalg.norm(np.array((iqx, idx)))
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
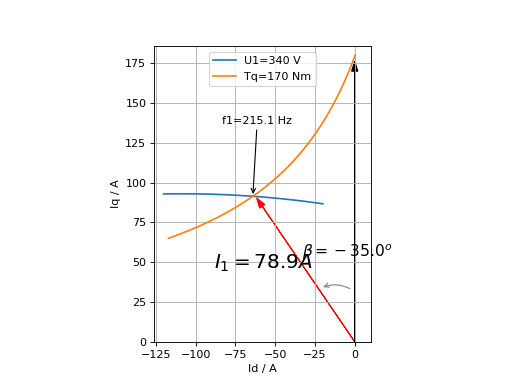
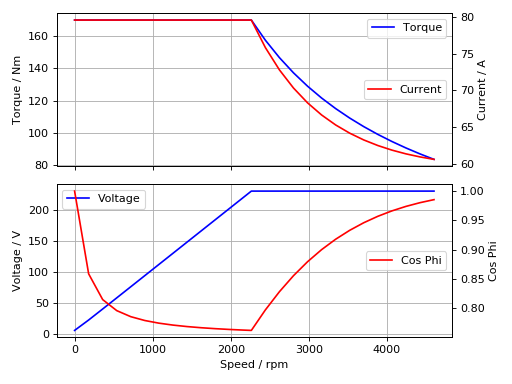
Speed-Torque characteristics with max power:
def torque(T, pmax, wm):
"""shaft torque as a function of rotor angular speed"""
if wm <= pmax / T:
return T
return pmax / wm
pmax = 60e3
n = np.linspace(0, 75, 20)
T = [torque(Tmax, pmax, 2*np.pi*nx) for nx in n]
r = pm.characteristics(T, n, u1)
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
Execute Parameter Variations¶
Example: calculate torque, torque ripple and iron losses at beta=-50°,-25°,0°:
parvar = {
"objective_vars": [
{"name": "dqPar.torque[-1]"},
{"name": "torque[-1].ripple"},
{"name": "machine.plfe[-1]"}],
"population_size": 3,
"decision_vars": [
{"steps": 3,
"bounds": [-50, 0],
"name": "angl_i_up"}
}
operatingConditions = dict(
angl_i_up=0.0,
calculationMode="pm_sym_fast",
wind_temp=60.0,
magn_temp=60.0,
current=50.0,
speed=50.0)
numcores = 3
engine = femagtools.multiproc.Engine(numcores)
mcvDir = os.path.join(
os.path.expanduser('~'), 'mcv')
g = femagtools.grid.Grid(workdir,
magnetizingCurves=mcvDir)
results = g(parvar, pmMachine,
operatingConditions, engine)
The variable results is a dict with the keys x and f holding the (n x m) arrays of the decision and the objective variables.
Make a Multi-Objective Optimization¶
Example: minimize ripple and losses and maximize torque (note the sign parameter) by varying magnet width and height
optdef = {
"objective_vars": [
{"name": "dqPar.torque[-1]", "desc": "Torque / Nm", "sign": -1},
{"name": "torque[0].ripple", "desc": "Torque Ripple / Nm"},
{"name": "machine.plfe[-1]", "desc": "Iron Loss / W" }
],
"population_size": 24,
"decision_vars": [
{"name": "magnet.magnetSector.magn_width_pct",
"desc": "Magn width",
"bounds": [0.75, 0.85]},
{"name": "magnet.magnetSector.magn_height",
"desc": "Magn height",
"bounds": [3e-3, 5e-3]}
]
}
engine = femagtools.condor.Engine()
opt = femagtools.opt.Optimizer(workdir,
magnetizingCurve, magnetMat)
num_generations = 3
results = opt.optimize(num_generations,
optdef, machine, operatingConditions, engine)