Leiteranordnung (AC)¶
Am Beispiel einer Leiteranordnung mit einem wirbelstromführenden Massivleiter wird die magnetodynamischen Berechnung (Fall f > 0) mit FSL veranschaulicht.
Folgende Beispiele können im Skript ausgewählt werden:
-- 30 = proximity effect in open conductors
-- 31 = induced current in short cicuited conductors
-- 32 = skin effect in a single conductor
-- 33 = skin effect in a coil
case = 31
- Bemerkungen
Die Randbedingungen sind physikalisch nicht sinnvoll, dieses Skript-Beispiel dient lediglich der Verdeutlichung.
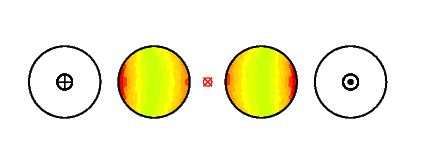
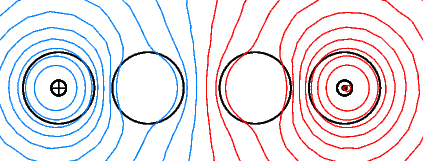
Wirbelstromdichte und Feldlinienverlauf im Falle offener Sekundärleiter (case = 30)
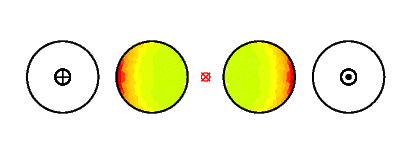
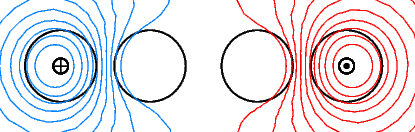
Wirbelstromdichte und Feldlinienverlauf im Falle kurzgeschlossener Sekundärleiter (case = 31)
Skript-Datei
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-- Allgemeine Einstellungen ----------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
exit_on_error = true -- Verhalten nach Fehler
exit_on_end = false -- Verhalten nach Skriptausfuehrung
verbosity = 2 -- Grad der Bildschirmmeldungen
tts = 1 -- minimum time to sleep between change of figures
-- choose type of problem -------------------------------------------------------
-- magnetodynamic with massiv conductors f!=0, v=0
-- 30 = proximity effect in open conductors
-- 31 = induced current in short cicuited conductors
-- 32 = skin effect in a single conductor
-- 33 = skin effect in a coil
case = 31
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-- Modellerstellung ------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
new_model_force("example13","FEMAG-AC FSL Example")
global_unit('mm') -- Globale Einheit (m; cm; mm)
pickdist(0.001) -- Abstand für Schnappen auf Knotenpunkt
cosys('polar') -- Beszugssystem
bA2 = 350
RLa = 20
RLi = 20
SW1 = 160
SW2 = 60
ndt(bA2/20) -- global node distance
dn = 3 -- node distance of conductors
nLa = math.ceil(2*math.pi*RLa/dn)+1
nLi = math.ceil(2*math.pi*RLi/dn)+1
x1 = bA2/2; y1 = 0.0;
x4 = -SW1/2; y4 = 0;
x6 = SW1/2; y6 = 0;
x3 = -SW2/2; y3 = 0;
x5 = SW2/2; y5 = 0;
nc_circle(x1,y1,-x1,y1,0)
nc_circle(-x1,y1,x1,y1,0)
nc_circle_m(x3,y3,RLi,nLi)
nc_circle_m(x4,y4,RLa,nLa)
nc_circle_m(x5,y5,RLi,nLi)
nc_circle_m(x6,y6,RLa,nLa)
adapt_window()
create_mesh()
def_bcond_vpo(x1,y1,-x1,y1)
def_bcond_vpo(-x1,y1,x1,y1)
if case<32 or case>33 then
Nc = 100
ff = 0.6
set_dev_data("cond_fillfact",ff*100,ff*100)
wk1 = def_new_wdg(x4,y4,"cyan","Spule 1",Nc,0,wi)
add_to_wdg(x6,y6,wsamekey,wo,wser)
if case<=30 or case==31 or case==40 or case==50 then
Jc = 4.5;
Ic = math.pi*RLa^2*ff/Nc*Jc
def_curr_wb(wk1,Ic,0)
end
end
wk2 = def_new_bar(x3,y3,lightgrey,"Spule 2",0,0,wi,58e6,1.0,100)
if case==30 or case==33 then
add_to_bar(x5,y5,wsamekey,wo,wser) -- offener Spule
end
if case==31 or case==40 or case==50 then
add_to_bar(x5,y5,wsamekey,wi,wpar) -- kurzgeschlosses Spule
end
if case==32 or case==33 then
Jb = 4.5;
Ib = math.pi*RLi^2*Jb
def_curr_wb(wk2,Ib,0)
end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-- Berechnen -------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
f1 = 100 -- max frequency
N = 5 -- number of frequency steps
state_of_problem("mag_static")
f = 0
calc_field_single(1,actual,0.01)
post_models("draw_f_lines","b")
sleep(tts)
state_of_problem("mag_dynamic")
for i=1,N do
color_gradation(0,0,"tot","ecurd",0,0,"")
f = f1*i/N
if case==21 or case==40 or case==50 then
set_mat_velo(x3,y3,0,f/50*2*math.pi)
set_mat_velo(x5,y5,0,f/50*2*math.pi)
end
calc_field_single(1,actual,0.01,f)
post_models("draw_f_lines","b")
save_metafile("field_lines_f.eps")
sleep(tts)
end
color_gradation(0,0,"tot","ecurd",0,0,"ecurr_dens_f.eps")
sleep(tts)
--save_model('close')
