Models¶
The models are dictionaries with the properties of a machine or a calculation.
Machine¶
Machines have a set of basic parameters, a stator, a magnet and a winding:
Parameter |
Description |
Unit |
|---|---|---|
name |
Name of machine |
|
lfe |
Lenght of iron |
m |
poles |
Number of poles |
|
outer_diam |
Outer diameter (yoke side) |
m |
bore_diam |
Bore diameter (airgap side) |
m |
inner_diam |
Inner diameter (yoke) |
m |
airgap |
airgap width |
m |
external_rotor |
True, False |
False |
ffactor |
processing factor for iron losses |
|
dxffile |
(see Model Creation with DXF) |
Stator¶
Stators have basic parameters and slots:
Parameter |
Description |
Default |
|---|---|---|
num_slots |
Number of Slots Q |
|
num_slots_gen |
Number of Slots in Model |
m*Q/gcd(Q, 2p*m) |
rlength |
Relative iron length |
1.0 |
mcvkey_yoke |
Name of lamination material |
dummy |
mcvkey_teeth |
Name of lamination material |
dummy |
nodedist |
Factor for node distance |
1.0 |
Note
if no value for num_slots_gen is given its value is calculated from the the number of slots Q and pole pairs p. (version added 0.0.16)
Stator Slots¶
Name |
Parameter |
|---|---|
stator1 |
slot_rf1, tip_rh1, tip_rh2, tooth_width, slot_width |
stator2 |
slot_t1, slot_t2, slot_t3, slot_depth, slot_width, corner_width |
statorRotor3 |
slot_height, slot_h1, slot_h2, slot_width, slot_r1, slot_r2, wedge_width1, wedge_width2, middle_line, tooth_width, slot_top_sh |
stator4 |
slot_height, slot_h1, slot_h2, slot_h3, slot_h4, slot_width, slot_r1, wedge_width1, wedge_width2, wedge_width3 |
statorBG |
yoke_diam_ins slot_h1, slot_h3, slot_width, slot_r1, slot_r2, middle_line, tooth_width, tip_rad, slottooth |
<filename> |
|
dxffile |
Note
All units are metric units.
User defined Stator Slots with FSL¶
If a FSL file that includes the definition of stator geometry exists and is readable it can be used for the model creation.
Example with file mystator.fsl:
machine = dict(
name="Motor",
...
stator=dict(
mcvkey_yoke='dummy',
mcvkey_shaft="dummy",
mystator=dict()
),
...
User defined Slots with DXF¶
If a DXF file that defines the stator geometry exists and is readable it can be used to create the FSL of the model. All DXF conversion parameters are supported.
Example:
machine = dict(
name="Motor",
...
stator=dict(
mcvkey_yoke='dummy',
dxffile=dict(
name="mystator.dxf",
position='out',
split=True
)
),
...
Parameters |
Description |
Default |
|---|---|---|
position |
‘in’ or ‘out’ |
|
split |
splits intersecting lines at their intersection-points |
False |
plot |
creates the plot of the integrated object |
False |
– Note:: The split option is required only if intersecting lines have no common point.
Windings¶
Name |
Parameter |
Default |
|---|---|---|
num_phases |
number of phases (m) |
|
num_wires |
number of wires per slot |
|
coil_span |
coil span |
|
num_layers |
number of layers |
|
cufilfact |
Fill factor of copper |
0.45 |
culength |
rel length of conductor |
1.4 |
cuconduc |
conductivity (S/m) |
56e6 |
slot_indul |
insulation thickness in slot |
0.0 |
Windings may contain a leakage dict: leak_dist_wind, leak_evol_wind, leak_tooth_wind (version added 0.9.9)
leak_dist_wind
Name
Parameter
Unit
perimrad
Radius of perimeter
m
vbendrad
Bending radius vertical
m
endheight
End winding height
m
m.wiredia
Wire diameter
m
leak_evol_wind
Name
Parameter
Unit
evol1rad
Top radius of first evolvent
m
evol2rad
Top radius of second evolvent
m
botlevel
Level at bottom of evolvents
m
toplevel
Level at top of evolvents
m
evolbend
Bending radius
m
endheight
End winding height
m
m.wiredia
Wire diameter
m
leak_tooth_wind
Name
Parameter
Unit
bendrad
Bending radius vertical
m
endheight
End winding height
m
m.wiredia
Wire diameter
m
Example:
windings=dict( num_phases=3, num_wires=100, coil_span=3.0, num_layers=1, leak_dist_wind=dict( perimrad=67.1e-3, # Radius of perimeter [m] vbendrad=5e-3, # Bending radius vertical [m] endheight=20e-3, # End winding height [m] wiredia=1e-3) # Wire diameter [m] )
Magnet¶
Magnets have basic parameters and slots:
Parameter |
Description |
Default |
|---|---|---|
mcvkey_yoke |
Name of lamination material |
dummy |
mcvkey_shaft |
Name of shaft material |
dummy |
material |
Name of magnet material |
|
nodedist |
Factor for node distance |
1.0 |
Note
the mcvkey parameters either reference a filename without extension (Example ‘M330-50A’) which must be found in the directory defined by the parameter magnetizingCurves of the Femag constructor or the name of an entry in the magnetizingCurve object.
the material parameter references a name of the ‘Magnet Material’_ list.
Rotor Slots¶
Name |
Parameter |
|---|---|
magnetSector |
magn_num, magn_width_pct, magn_height, magn_shape, bridge_height, magn_type, condshaft_r, magn_ori, magn_rfe, bridge_width, magn_len |
magnetIron |
magn_height, magn_width, gap_ma_iron, air_triangle, iron_height, magn_rem, condshaft_r, magn_ori, bridge_height, bridge_width, iron_shape |
magnetIron2 |
magn_height, magn_width, gap_ma_iron, air_triangle, iron_height, magn_rem, condshaft_r, gap_ma_right, gap_ma_left, magn_ori, iron_shape |
magnetIron3 |
magn_height, iron_bfe, gap_ma_iron, air_triangle, iron_height, gap_ma_right, gap_ma_left, condshaft_r, magn_num, magn_ori, iron_shape |
magnetIron4 |
magn_height, magn_width, gap_ma_iron, iron_shape, air_space_h, iron_bfe, magn_di_ra, corner_r, air_sp_ori, magn_ori, magn_num |
magnetIron5 |
magn_height, magn_width, gap_ma_iron, iron_bfe, air_space_h, corner_r, air_sp_ori, magn_num, iron_shape, air_space_b, magn_di_ra |
magnetIronV |
magn_height, magn_width, magn_angle, magn_num, iron_hs, iron_height, iron_shape, air_triangle, gap_ma_iron, magn_rem, condshaft_r |
magnetFC2 |
yoke_height, iron_h1, iron_h2, iron_b, magn_width, magn_height, iron_bfe, iron_bfo, iron_shape, iron_hp, magn_num |
<filename> |
|
dxffile |
Example:
machine = dict(
name="PM 130 L4",
lfe=0.1,
poles=4,
outer_diam=0.13,
bore_diam=0.07,
inner_diam=0.015,
airgap=0.001,
stator=dict(
num_slots=12,
num_slots_gen=3,
mcvkey_yoke="dummy",
rlength=1.0,
stator1=dict(
slot_rf1=0.057,
tip_rh1=0.037,
tip_rh2=0.037,
tooth_width=0.009,
slot_width=0.003)
),
magnet=dict(
mcvkey_shaft="dummy",
mcvkey_yoke="dummy",
magnetSector=dict (
magn_num=1,
magn_width_pct=0.8,
magn_height=0.004,
magn_shape=0.0,
bridge_height=0.0,
magn_type=1,
condshaft_r=0.02,
magn_ori=2,
magn_rfe=0.0,
bridge_width=0.0,
magn_len=1.0 )
),
windings=dict(
num_phases=3,
num_wires=100,
coil_span=3.0,
num_layers=1)
)
User defined Magnet Slots with FSL¶
Example
If a FSL file that creates the magnet geometry exists and is readable it can be used for the model creation as an empty dict:
machine = dict(
name="Motor",
...
magnet=dict(
mcvkey_yoke='dummy',
mcvkey_shaft="dummy",
myrotor=dict()
),
...
User defined Slots with DXF¶
If a DXF file that defines the magnet geometry exists and is readable it can be used to create the FSL for the model.
Example:
machine = dict(
name="Motor",
...
magnet=dict(
mcvkey_yoke='dummy',
mcvkey_shaft="dummy",
dxffile=dict(
name='mymagnet.dxf',
position='in',
split=True
)
),
...
Parameters |
Description |
Default |
|---|---|---|
position |
‘in’ or ‘out’ |
|
split |
splits intersecting lines at their intersection points |
False |
plot |
creates the plot of the integrated object |
False |
– Note:: The split option is required only if intersecting lines have no common point.
Magnetizing Curve¶
The MagnetizingCurve is a container of magnetizing curves (eg. lamination or PM material) that can be referenced by the model mcvkey attributes. It can either point to a directory of MC/MCV-File or hold a list of magnet curves which are identified by name.
Each magnetizing curve is described by the following properties
Attribute |
Description |
Unit |
Default |
|---|---|---|---|
name |
Identifier of this curve |
||
ctype |
Type of curve |
1 |
|
desc |
Description |
||
curve |
List of dictionaries with bi (list of induction values) hi (List of field strength values) and angle which can be missing in case of 1 curve |
T, A/m, deg |
|
ch |
hysteresis loss factor |
0 |
|
cw |
eddy current loss factor |
0 |
|
ch_freq |
hysteresis exponent |
0 |
|
cw_freq |
eddy-current exponent |
0 |
|
b_coeff |
induction loss exponent |
0 |
|
Bo |
reference induction |
T |
1.5 |
fo |
reference frequency |
Hz |
50 |
fillfac |
iron fill factor |
1 |
|
bsat |
saturation induction |
T |
2.15 |
rho |
specific weight |
kg/dm3 |
7.65 |
The loss factors and exponents are used in the Jordan loss calculation formula:
(cw*(f/fo)**cw_freq + ch*(f/fo)**ch_freq)*(B/Bo)**b_coeff
The Reader object which is included in the mcv module can be used to read MCV/MC files.
Permeability and polarisation calculation example:
MUE0 = 4e-7*math.pi
mcv = femagtools.mcv.Reader()
mcv.readMcv('magnetcurves/M270-35A.MCV')
r = mcv.get_results()
bh = [(bi, hi)
for bi, hi in zip(r['curve'][0]['bi'],
r['curve'][0]['hi']) if bi > 0 and hi > 0]
ji = [b-MUE0*h for b, h in bh]
muer = [bx/hx/MUE0 for bx, hx in bh]
Using a magnetizingcurve to write a mcv file:
mcvData = dict(curve=[ dict(
bi=[0.0, 0.09, 0.179, 0.267, 0.358,
0.45, 0.543, 0.6334, 0.727,
0.819, 0.9142, 1.0142, 1.102,
1.196, 1.314, 1.3845, 1.433,
1.576, 1.677, 1.745, 1.787,
1.81, 1.825, 1.836],
hi=[0.0, 22.16, 31.07, 37.25, 43.174,
49.54, 56.96, 66.11, 78.291,
95, 120.64, 164.6, 259.36,
565.86, 1650.26, 3631.12, 5000, 10000,
15000, 20000, 25000, 30000, 35000, 40000]
)],
name='m270-35a',
desc=u"Demo Steel",
ch=4.0,
cw_freq=2.0,
cw=1.68)
mcv = femagtools.mcv.MagnetizingCurve(mcvData)
mcv.writefile('m270-35a')
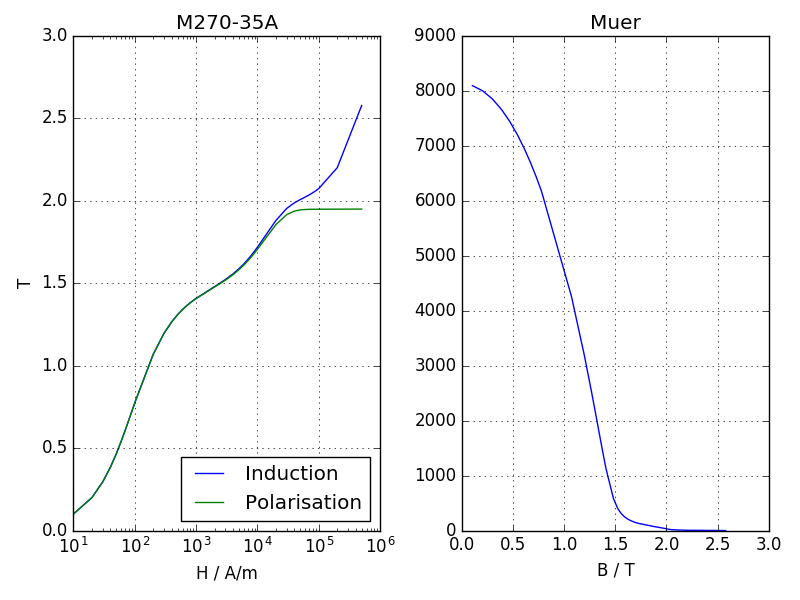
Note
if the curve data is used in a stator or magnet slot model there is no need to create the file explicitly. Femagtools will take care of that during the model creation.
Magnet Material¶
list of dict objects each having a unique name (or id) and a set of parameters that describe the magnet properties.
Parameter |
Description |
Default |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
name |
Name of magnet material |
||
mcvkey |
name of nonlinear B(H) curve |
||
orient |
Magnetizing orientation |
cartiso |
|
rlen |
Relative length |
1.0 |
|
remanenc |
Remanence Induction Br |
T |
|
relperm |
Relative Permeability |
||
spmaweight |
Specific Mass |
7500 |
kg/m³ |
temcoefbr |
Temperature Coefficient of Br |
-0.001 |
1/K |
temcoefhc |
Temperature Coefficient of Hc |
-0.001 |
A/m/K |
magntemp |
Magnet Temperature |
20 |
°C |
magncond |
Electr. Conductivity |
625000 |
S/m |
magnwidth |
Magnet width |
0.0 |
m |
magnlength |
Magnet length in z direction |
0.0 |
m |
Note
name must be unique within list. It may be used as reference in the magnet model of the machine.
Example:
magnets = [dict(name='MX-333', remanenc=1.2, relperm=1.05)]
mcvkey is used for material that have a non-linear BH curve.
the key orient describes the field orientation (mcartiso, mpoliso, martaniso, mpolaniso)
rlen defines the relative length
Example:
magnets=[dict(name='BH53M', mcvkey='BH53M', orient='mcartiso', rlen=1.0)]
The mcvkey can either reference a file or an entry in the magnetizing curve dict.
User Specified Magnet Geometries¶
Magnet geometries not covered by the built in models can be specified by fsl code. Here is a example:
The steps are:
Create a diagram of the geometry and decide about the parameters to be used.
Create a fsl mako template file with the chosen parameters as placeholders using the Mako syntax with ${}.
Include this filename in the magnet model within the section using the basename of the mako file and set the parameter values.
The following values are defined globally and can be referenced in the template:
Name |
Description |
Unit |
|---|---|---|
mcvkey_yoke |
lamination material of yoke |
|
mcvkey_shaft |
material of shaft |
|
m.remanenc |
Remanence Induction |
T |
m.relperm |
Rel. Permeability of PM |
|
m.num_poles |
Number of poles |
|
m.npols_gen |
Number of poles in model |
|
agndst |
Node distance in airgap |
m |
dy1 |
Diameter of stator yoke |
m |
da1 |
Diameter of stator bore |
m |
da2 |
Diameter of rotor |
m |
dy2 |
Diameter of rotor yoke |
m |
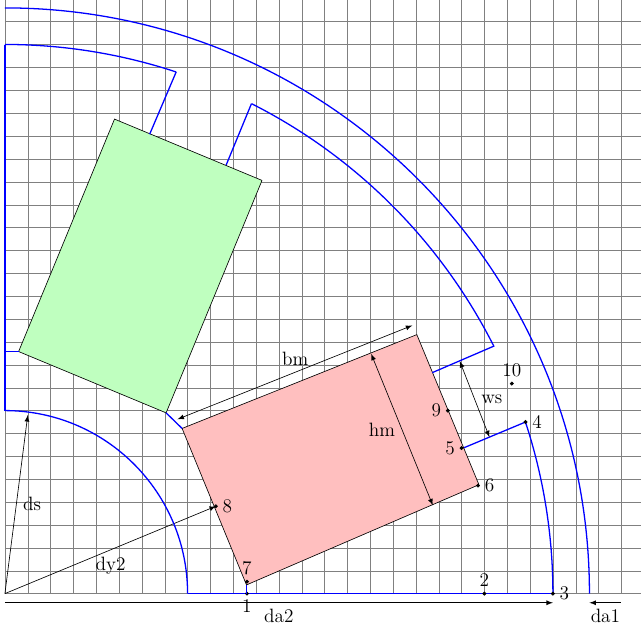
Example FSL Template file ‘’spoke.mako’’ using 4 parameters:
-- Model parameters
ds = ${model['shaft_diam']}*1e3
hm = ${model['magn_height']}*1e3
bm = ${model['magn_width']}*1e3
ws = ${model['slot_width']}*1e3
-- calculate slot height and pole pitch
hs = (da2-dy2)/2 - bm
taup = math.pi/m.num_poles
x = {}
y = {}
-- characteristic points of model
ar = math.sqrt(dy2^2+hm^2)/2
x[1] = ar*math.cos(taup - math.atan2(hm/2, dy2/2))
y[1] = 0
x[2],y[2] = pr2c(dy2/2+bm, 0)
x[3],y[3] = pr2c(da2/2, 0)
x[4],y[4] = pr2c(da2/2, taup - math.atan2(ws/2,(da2/2)))
x[5],y[5] = pr2c(da2/2-hs, taup - math.atan2(ws/2,(da2/2 - hs)))
x[6],y[6] = pr2c(da2/2-hs, taup - math.atan2(hm/2, da2/2-hs))
x[7],y[7] = pr2c(ar, taup - math.atan2(hm/2, dy2/2))
x[8],y[8] = pr2c(dy2/2, taup)
x[9],y[9] = pr2c(da2/2 - hs, taup)
x[10],y[10] = pr2c(da2/2, taup)
Magnet definition in Python file with included mako file (eg in this case ‘’spoke’’) and the parameter definition:
..
magnet=dict(
mcvkey_yoke="dummy",
spoke=dict(
magn_height=0.008,
shaft_diam=0.01,
slot_width=0.004,
magn_width=0.024
)
..
The resulting model:
Note
Starting with Release 0.4.4 the syntax has changed but backward compatibility is fully supported.
the complete example can be found in stator1-spoke.py and spokefml.mako in the example directory on github.
FE-Simulation¶
Cogging (cogg_calc)
Parameter |
Description |
Default |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
speed |
Speed |
1/s |
|
skew_angle |
Skewing angle |
0 |
deg |
num_skew_steps |
Number of skew steps |
0 |
|
magn_temp |
Magnet Temperature |
°C |
|
num_move_steps |
Number of move steps |
||
num_par_wdgs |
Number of parallel windings |
1 |
|
eval_force |
Evaluate force |
0 |
|
period_frac |
Rotate Fraction of Period |
1 |
|
vtu_movie |
Create VTU files |
False |
Example:
operatingConditions = dict(
calculationMode="cogg_fast",
magn_temp=60.0,
num_move_steps=49,
speed=50.0)
PM/Rel Machine Simulation (pm_sym_fast)
Parameter |
Description |
Default |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
speed |
Speed |
1/s |
|
skew_angle |
Skewing angle |
0 |
deg |
num_skew_steps |
Number of skew steps |
0 |
|
magn_temp |
Magnet Temperature |
°C |
|
wind_temp |
Winding Temperature |
20 |
°C |
num_move_steps |
Number of move steps |
49 |
|
num_par_wdgs |
Number of parallel windings |
1 |
|
eval_force |
Evaluate force |
0 |
|
explicit_mode |
Activates/deactivates step adjustments |
0 |
|
current |
Phase current |
A (RMS) |
|
angl_i_up |
Angle I vs. Up |
0 |
deg |
optim_i_up |
Optimize Current |
0 |
|
phi_start |
Start angle of rotation |
0 |
deg |
range_phi |
Rotation angle |
360/p |
deg |
explicit_mode |
Deactivate rotation correction |
0 |
|
plots |
Create plots |
[] |
|
airgap_induc |
calculate airgap induction |
False |
|
period_frac |
Rotate Fraction of Period |
1 |
|
vtu_movie |
Create VTU files |
False |
Note
plots is a list of field_lines or color_gradation plots to be created after the calculation. Possible values ‘field-lines’, ‘Babs’, ‘Br’, ‘Bx’, ‘By’, ‘Br’, ‘Bt’, ‘Habs’, ‘Hx’, ‘Hy’, ‘Hr’, ‘Ht’ ‘demag’, ‘ecurr’, ‘ecloss’, ‘relperm’, ‘Wm’, ‘Bdev’, ‘Vpot’. (See http://script.profemag.ch/ColorGrad.html) added in version 0.0.16. The value types can be simple strings or list with name and min/max range.
Example:
operatingConditions = dict(
calculationMode="pm_sym_fast",
wind_temp=60.0,
magn_temp=60.0,
current=50.0,
speed=50.0,
plots=['field_lines', ['Babs', 0.0, 2.5]])
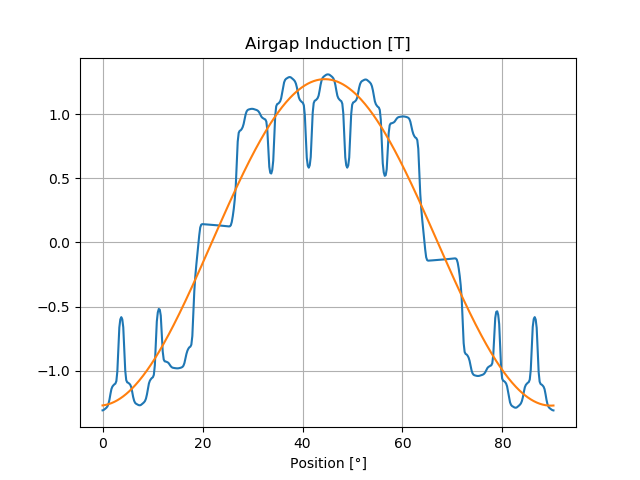
Note
If airgap_induc is True the induction in the airgap is calculated after the simulation returns. The values can be read with the method read_airgap_induc() of call Femag.
Parameter |
Description |
Unit |
|---|---|---|
Baml |
Amplitude of base harmonic |
T |
phi0 |
Phase angle of base harmonic |
rad |
pos |
Position |
° or mm |
B |
sampled values |
T |
B_fft |
Values of base harmonic |
T |
Short circuit calculation (shortcircuit)
The short circuit calculation is executed subsequentially to a pm_sym_fast simulation if shortCircuit is set True. (version added 0.9.30). The results are included in scData dict of bch
Parameter
Description
Default
Unit
shortCircuit
run short circuit calc if True
l_end_winding
winding inductance
0
H
l_external
External inductance
0
H
sc_type
type of short circuit (3-phase)
3
simultime
Simulation time
0.1
s
initial
Initial condition 1: noload 2: load
2
allow_demagn
Allow Demagnetisation:1:yes; 0:no
0
sim_demagn
Simulate Demagnetisation:1:yes; 0:no
0
Example:
pmRelSim = dict( angl_i_up=-39.3, calculationMode="pm_sym_fast", wind_temp=60.0, magn_temp=60.0, current=76.43, period_frac=6, speed=50.0, shortCircuit=True, l_end_winding=0, l_external=0, sc_type=3, initial=2, allow_demagn=0, sim_demagn=1) r = femag(machine, pmRelSim) print('Torque [Nm] = {}'.format(r.machine['torque'])) print(''' Short Circuit Current Torque Peak iks {2:8.1f} A tks {3:8.1f} Nm Stationary ikd {0:8.1f} A tkd {1:8.1f} Nm peak winding currents {4} '''.format(r.scData['ikd'], r.scData['tkd'], r.scData['iks'], r.scData['tks'], r.scData['peakWindingCurrents'])) fig, ax = plt.subplots() femagtools.plot.transientsc(r) plt.show()
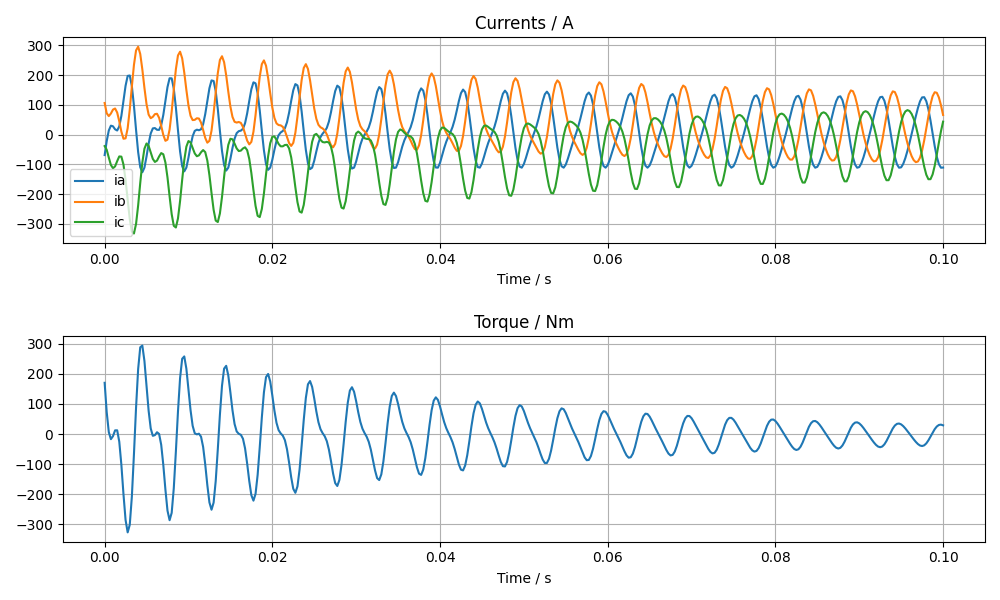
Ld-Lq Identification (ld_lq_fast)
Parameter |
Description |
Default |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
speed |
Speed |
1/s |
|
skew_angle |
Skewing angle |
0 |
deg |
num_skew_steps |
Number of skew steps |
0 |
|
magn_temp |
Magnet Temperature |
°C |
|
num_move_steps |
Number of move steps |
||
num_par_wdgs |
Number of parallel windings |
1 |
|
eval_force |
Evaluate force |
0 |
|
i1_max |
Max. phase current |
A (RMS) |
|
beta_min |
Min. Beta angle |
deg |
|
beta_max |
Max. beta angle |
deg |
|
num_cur_steps |
Number of current steps |
||
num_beta_steps |
Number of beta steps |
||
period_frac |
Rotate Fraction of Period |
1 |
Example:
feapars = dict(
num_move_steps=25,
calculationMode="ld_lq_fast",
magn_temp=60.0,
i1_max=150.0,
beta_max=0.0,
beta_min=-60.0,
num_cur_steps=3,
num_beta_steps"=4,
speed=50.0)
Psid-Psiq Identification (psd_psq_fast)
Parameter |
Description |
Default |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
speed |
Speed |
1/s |
|
skew_angle |
Skewing angle |
0 |
deg |
num_skew_steps |
Number of skew steps |
0 |
|
magn_temp |
Magnet Temperature |
°C |
|
num_move_steps |
Number of move steps |
||
num_par_wdgs |
Number of parallel windings |
1 |
|
eval_force |
Evaluate force |
0 |
|
maxid |
Max. Amplitude Id current |
A |
|
minid |
Min. Amplitude Id current |
A |
|
maxiq |
Max. Amplitude Iq current |
A |
|
miniq |
Min. Amplitude Iq current |
A |
|
delta_id |
Delta of Id current steps |
A |
|
delta_iq |
Delta of Iq current steps |
A |
|
period_frac |
Rotate Fraction of Period |
1 |
Example:
feapars = dict(
num_move_steps=25,
calculationMode="psd_psq_fast",
magn_temp=60.0,
maxid=0.0,
minid=-150.0,
maxiq=150.0
miniq=0.0,
delta_id=50.0,
delta_iq=50.0,
speed=50.0)
PM/Rel Torque Calc (torq_calc)
Parameter |
Description |
Default |
Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
speed |
Speed |
1/s |
|
skew_angle |
Skewing angle |
0 |
deg |
num_skew_steps |
Number of skew steps |
0 |
|
magn_temp |
Magnet Temperature |
°C |
|
wind_temp |
Winding Temperature |
20 |
°C |
num_move_steps |
Number of move steps |
49 |
|
num_par_wdgs |
Number of parallel windings |
1 |
|
current |
Phase current |
A (RMS) |
|
angl_i_up |
Angle I vs. Up |
0 |
deg |
Example:
operatingConditions = dict(
calculationMode="torq_calc",
wind_temp=60.0,
magn_temp=60.0,
current=50.0,
angl_i_up=0.0,
speed=50.0)
FE-Simulation with existing model¶
FE calculations can be executed for existing models also. Since Femag Rel 8.3 there is no need to fully specify the machine model:
machine = "PM 270 L8"
workdir = os.path.join(
os.path.expanduser('~'), 'femag')
femag = femagtools.Femag(workdir)
operatingConditions = dict(
angl_i_up=-38.7,
calculationMode="pm_sym_fast",
magn_temp=60.0,
num_move_steps=25,
speed=50.0,
wind_temp=60.0,
current=108.0)
r = femag(machine,
operatingConditions)
For older FEMAG versions the minimal data is:
machine = dict(
name="PM 130 L4",
lfe=0.1,
poles=4,
outer_diam=0.13,
bore_diam=0.07,
airgap=0.001,
stator=dict(
num_slots=12,
num_slots_gen=3,
mcvkey_yoke="dummy"
)
)
Model Creation with DXF¶
The goal of the dxfsl modules is to create a complete FE model for rotating PM and Reluctance Machines on the basis of a DXF file with as little restrictions as possible. This has the consequence that symmetries, subregions, magnets, windings, boundary conditions need to be identified.
The procedure is as follows:
Read the DXF file and create a graph object with nodes and edges.
Identify the areas stator, rotor and airgap and their symmetry axis.
Add auxiliary lines if required by the meshing process.
Convert the graph object into FSL code including the identified subregions.
For monitoring and trouble-shooting purposes it is possible to create plots that display the intermediate results.
Example with a single dxf file motor.dxf:
machine = dict(
name="Motor",
lfe=0.001,
dxffile=dict(
name='motor.dxf'
),
stator=dict(
mcvkey_yoke='dummy',
mcvkey_shaft="dummy"
),
magnet=dict(
mcvkey_yoke="dummy",
mcvkey_shaft="dummy"
),
...
Note
The parameters poles, outer_diam, bore_diam and airgap as well as num_slots and num_slots_gen will be set automatically
Example with two separate dxf files for stator and rotor:
machine = dict(
name="Motor",
lfe=0.001,
stator=dict(
mcvkey_yoke='dummy',
dxffile=dict(
name='mystator.dxf',
position='out',
split=True
)
),
magnet=dict(
mcvkey_yoke="dummy",
mcvkey_shaft="dummy",
dxffile=dict(
name='myrotor.dxf',
position='in',
split=True
)
),
...